What is Cloud ERP?
Cloud ERP is an enterprise business application that is hosted on remote servers and accessed over the internet with a web browser.
Cloud ERP at a glance:
- Flexible, scalable, and easy to support and maintain
- Low upfront, all-inclusive price (SaaS license)
- Reduced IT complexity (Managed Services)
- Quick response to market changes with less IT concerns

This is a Heading
What are the Cloud ERP Deployment Models?
Multi Tenant (MT) SaaS - Public Cloud
- Economies of Scale,
- Ease of maintenance,
- Low and all-inclusive upfront price,
- Automated, fast Upgrades and technical updates,
- Extensibility of Vendor platform.
- Keep in mind:
- Less customizable (source code modification is forbidden in MT SaaS),
- May lack certain, unique Regulatory Compliance needs (i.e. certain DoD Contractor’s),
- Extensibility requires learning new methods and tools if custom capabilities and/or 3rd party app integrations are required.
Single Tenant (ST) SaaS - Private Cloud
The main difference between ST SaaS and MT SaaS is how the ERP is shared. With ST you own the version of the ERP software, and is dedicated to your organization only. Essentially, the businesses’ data is stored on private servers running its own instance.
The main benefits of Economies of Scale, for both the ERP Vendor and ERP consumer, are broken with Private Cloud.
- Strengths: More customizable (source code modification is allowed in ST SaaS), internal security controls can be higher, more flexible to upgrade or not.
- Keep in mind: Higher cost to maintain, higher SaaS fee price, no economies of scale.
Public Cloud
This refers to cloud services owned and operated by a contracted service provider. Each organization's data and applications are kept secure and separated from other companies.
- Strength: It offers excellent scalability and cost efficiency due to shared resources and a pay-as-you-go model.
- Keep in mind: Higher cost up front as you ‘own’ the software.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a dedicated cloud environment that is exclusively used by your organization, and computing resources are not shared with others.
- Strength: It provides greater control over security and customization, as the infrastructure is tailored to the organization’s specific requirements.
- Keep in mind: The investment and operational costs tend to be higher (as again you own the software).
Hybrid ERP
Combines on-premises ERP software with cloud-based services——for computing, storage, and other functionalities. Some say this merging of environments can be the best of both worlds.
- Strength: Offers flexibility by optimizing and balancing workloads between on-premises and cloud environments according to needs.
- Keep in mind: Managing and integrating the different systems can be complex, potentially leading to increased IT overhead and integration challenges.
How Cloud ERP Benefits Your Business?
Implementing Cloud ERP offers a wide array of benefits that can transform the way a business operates:
Efficient Business System
Cloud ERP brings everything under one ‘roof’ (central hub). Routine tasks are automated, departments work more closely together, and everyone—from finance teams to inventory managers—have real-time access to vital information, any where, anytime.
- Keep in mind: Integration with existing legacy systems and machines may require careful planning and phased implementation.
Flexibility for Growth
One of the biggest perks of Cloud ERP is scalability. As your business expands, the system adjusts to your growing needs without major overhauls to your IT infrastructure.
Keep in mind: Ensure that the chosen solution can handle both current and future needs, particularly when integrating emerging technologies like AI or machine learning.
Predictable Cost
Traditional ERP systems often require a hefty initial investment and ongoing maintenance fees. On the other hand, Cloud ERP usually operates under a subscription model. This lowers the entry costs and also shifts costs from capital expenditure to more manageable operational expenses—an attractive option especially for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Keep in mind: Evaluate the TCO carefully, accounting for hidden costs such as customization, integration, training, and potential downtime during migration.
More Efficient Customer Service
When all departments are working from the ‘same song sheet”, customer service naturally improves. With information at their fingertips, support teams can resolve issues faster and more efficiently, leading to happier, more loyal customers.
Keep in mind: Integrated customer relationship management (CRM) systems will maximize service improvements.


Bringing Everything Together
- Keep in mind: Implementing a Cloud ERP system can bring organizational challenges, such as resistance to change. During the implementation process, it’s crucial to ensure that all departments are well-informed about the new system, its capabilities, and the benefits it can bring. This proactive communication helps facilitate smoother adoption and minimizes pushback.
Enhanced Cybersecurity
Robust Security Standards: Cloud providers (like AWS) can afford the very best security measures.
Disaster Recovery: Minimized downtime with built-in disaster recovery.
Automatic Backups: Reduce your daily maintenance.
- Keep in mind: Verify that your cloud provider adheres to industry-specific compliance standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and includes advanced security protocols such as multi-factor authentication and identity management.

Transition from Legacy Systems to Cloud ERP
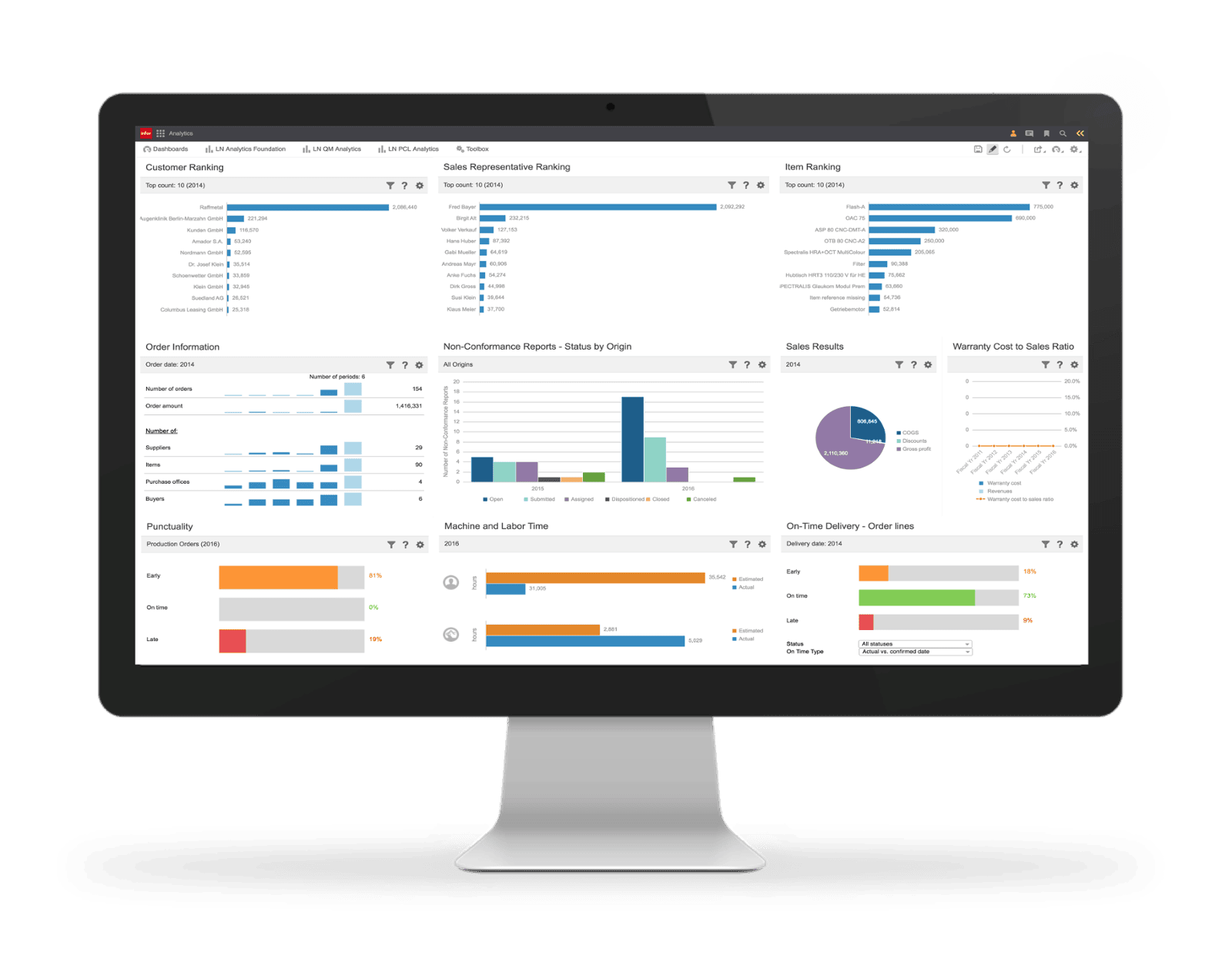
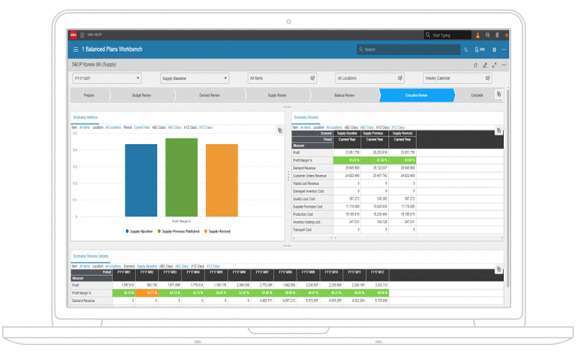
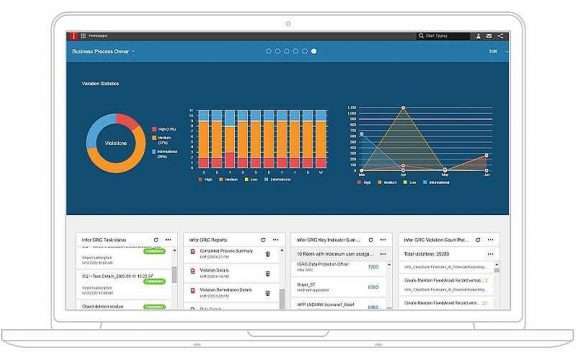
Meet with Infor CloudSuite Industrial
Infor CloudSuite (Syteline) is a powerful Cloud ERP solution designed specifically for SMB manufacturers, project management teams, and field service organizations. Many customers replace multiple separate data silos with this integrated, end-to-end ERP system that streamlines operations and manages all aspects of their business.